In the world of welding, precision and quality are paramount. Whether it’s constructing a skyscraper, assembling a ship, or crafting intricate metalwork, the integrity of welds is crucial. At the heart of this precision lies the welding electrode, and behind the scenes, the unsung hero: welding electrode making machinery.

The Evolution of Welding Electrodes
Welding electrodes are essential consumables in various industries, ranging from construction to manufacturing. They come in various types, each tailored to specific welding applications. These electrodes are primarily responsible for conducting the electrical current required for the arc and, in some cases, providing filler material.
Over the years, welding electrodes have evolved significantly, driven by advances in technology and the need for higher quality and efficiency. Modern electrodes are not just pieces of metal; they are highly engineered products with specific chemical compositions, coatings, and characteristics designed to meet demanding welding requirements.
The Role of Welding Electrode Making Machinery
Behind every high-quality welding electrode is a sophisticated manufacturing process, and at the heart of this process are the machines that make it all possible. Welding electrode making machinery plays a pivotal role in transforming raw materials into finished electrodes ready for welding.
1. Wire Drawing Machines
The journey of a welding electrode begins with wire drawing machines. These machines pull raw materials, typically mild steel or stainless steel wire, through a series of dies to reduce their diameter and improve their surface finish. The resulting wire is not only dimensionally precise but also possesses the required mechanical properties.
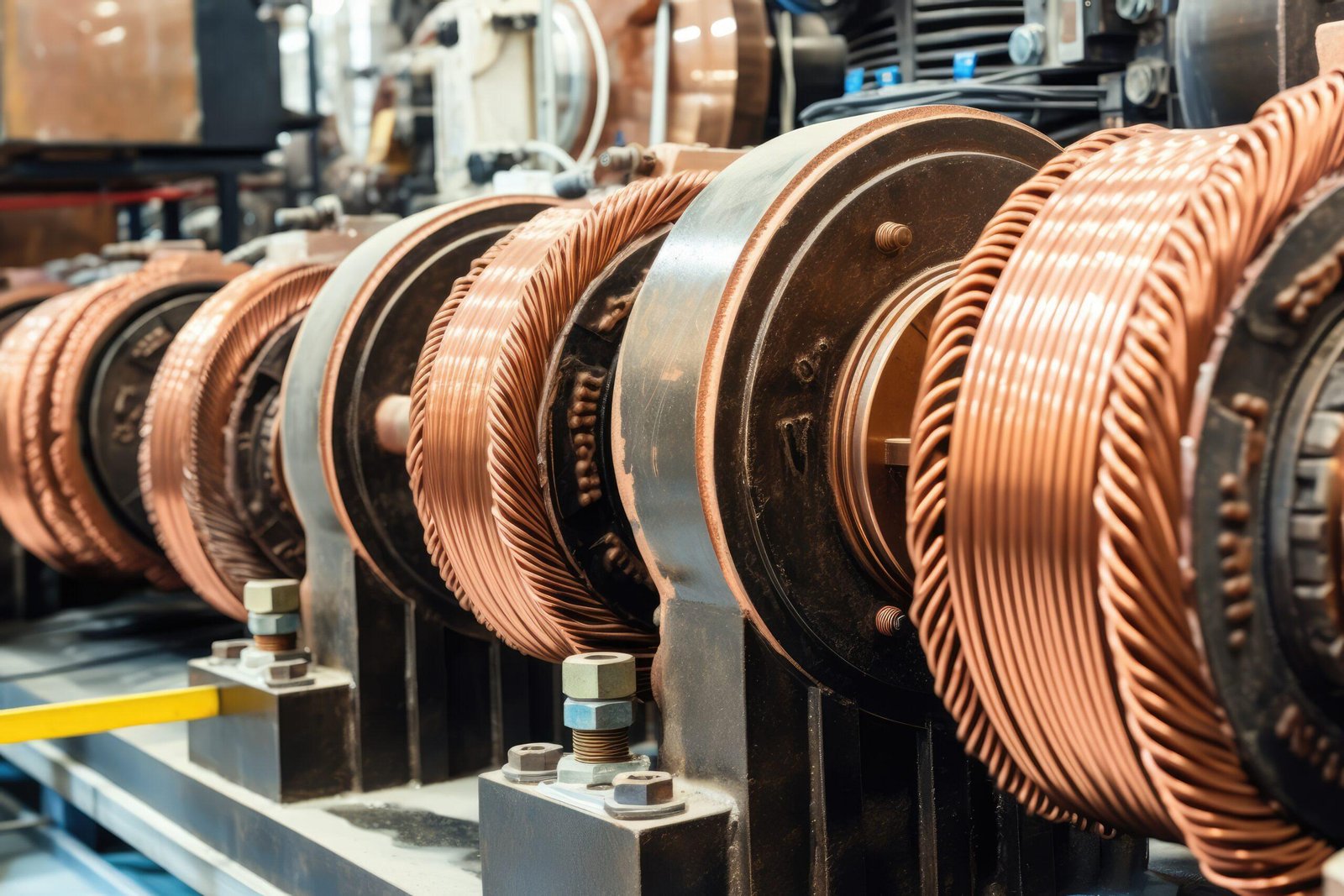
2. Coating Preparation
Many welding electrodes require specialized coatings to enhance their performance. This is where coating preparation machinery comes into play. These machines apply specific chemicals and fluxes to the electrode’s core wire, creating a uniform and controlled coating. The coating not only acts as a shield to protect the weld pool but also influences the electrode’s arc stability and ease of use.
3. Extrusion Presses
The core wire, now coated, needs to be shaped into the final electrode form. Extrusion presses are employed for this task. They use immense pressure to force the coated wire through a specially designed die to create the desired electrode shape and diameter.
4. Baking Ovens
Following extrusion, the freshly formed electrodes undergo a critical phase—baking. Baking ovens are used to heat-treat the electrodes, ensuring that they achieve the right mechanical properties and moisture content. This step is vital to guarantee the electrode’s performance and longevity.
5.Packaging and Quality Control
Before reaching the end-users, welding electrodes go through rigorous quality control checks. Specialized machinery assesses various parameters, such as coating thickness, diameter, and straightness. Once approved, the electrodes are packaged using automated equipment, ready for distribution.

Precision and Innovation
In an industry where weld quality directly impacts safety and structural integrity, precision and innovation in welding electrode making machinery are crucial. Manufacturers are constantly pushing the boundaries to produce electrodes that offer better arc stability, reduced spatter, and improved mechanical properties.
Environmental Considerations
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility in welding electrode manufacturing. Modern machinery is designed with energy efficiency in mind, and efforts are made to minimize waste and emissions throughout the production process.
Conclusion
Welding electrode making machinery may operate behind the scenes, but its significance in ensuring the quality and reliability of welding cannot be overstated. As technology advances and industry demands evolve, these machines will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of welding. From wire drawing to extrusion and coating, each step in the manufacturing process contributes to the creation of electrodes that welders can rely on for precision, strength, and durability.





